Reporting with multiple currencies
What it means when ‘Multi-Currency’ is displayed in a cell and how to display these values.
Reporting on multiple currencies is problematic because you can’t really add £10 to $10 without first converting them both into the same base currency. Yes 10+10 is 20 but 10 Euros does not equate to 10 Dollars, so we need to take the exchange rate into consideration. This is why we built some tools into reporting to help with this.
Workbooks warns you when a report calculates a value across more than one currency by displaying “Multi-currency” in the cell. This can occur when the report is first defined, or later when the records contain values in more than one currency. There are a variety of solutions to this problem.
Summarising financial transactions
Workbooks financial transactions are defined in a “document currency”: the currency that all of the line items are declared in and that the customer pays in, or that the supplier is paid in. Transactions also have a “home currency” that the line item values are converted to, so that you can estimate the value of the transactions in your own currency. For many companies this simple distinction means that you can easily report on the home currency values to ensure that you calculate values in one consistent currency.
Best practice is always to use home currency, even if you’ve only got one currency in use, in case another is added at a later date.
The home currency is attached to an Own Organisation – the Own Organisation operates in that currency for tax purposes. You may have more than one Own Organisation, for example one for each currency zone in which you are recognising revenue. If you have multiple Own Organisations, then you likely have multiple currencies and will need to ensure that your reports are designed with that in mind.
When adding a currency column to a report, you will see options for both home and document currency:
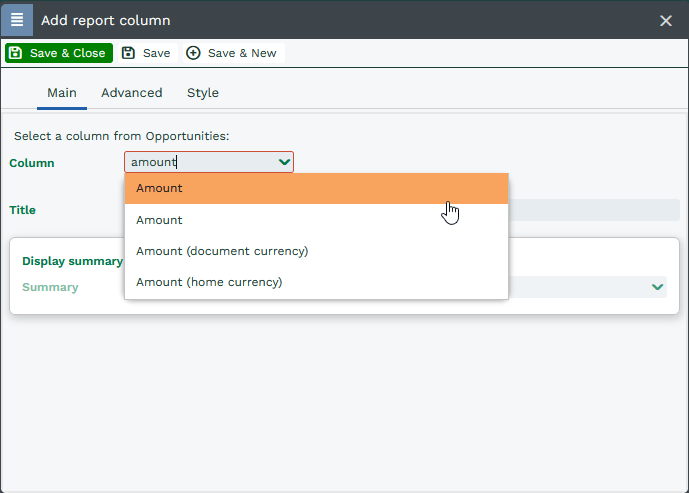

Wholly independent subsidiaries in each tax jurisdiction can be represented by Own Organisations, and so employees in each location may create their own reports to analyse transactions in their Own Organisation. Because these reports will have criteria to restrict the set of transactions to those in the Own Organisation, all of the transactions will have the same home currency, thus ensuring that the calculations are valid.
If you wish to create reports that combine transactions across multiple currencies in one report, then you must make sure that you separate the values by currency. For example you can group by the home currency of the transactions to produce separated totals.
Summarising other currency values
Currency values in records other than transaction documents and custom field currency values are not forced to a particular currency. To create reports on these currency fields you must decide on a convention that controls the currencies of these values to ensure that they can be combined in reports later.
Where the user can choose a currency for a field, Workbooks only offers a choice of the currencies defined on the Own Organisations in the database. So, for a single-currency database this issue is avoided very simply: the user can only choose that one currency.
In a database with multiple currencies you must train your users to choose a currency according to your business needs. For a custom field currency value on a transaction document or a line item we would recommend that it should hold a value in the document currency because the user will probably know or be able to calculate it easily.
Converting currencies
If you want to report across multiple Own Organisations that have different Home Currencies, or perhaps have custom document currency values that need converting to the Home Currency, you will need to make use of the CONVCURRENCY function in reporting. This function will convert a currency value into a different currency, using the exchange rate from a specified date.
The syntax to use is:
CONVCURRENCY(currency field, new currency, date)
For example, if I want to convert an Invoice’s Net Value, which is currently in its Home Currency of GBP, to my Parent Own Organisation’s Home Currency of USD, based on the Exchange Rate in place at the time of the Invoice Date, I would use the following:
CONVCURRENCY(home_currency_net_value, ‘USD’, document_date)
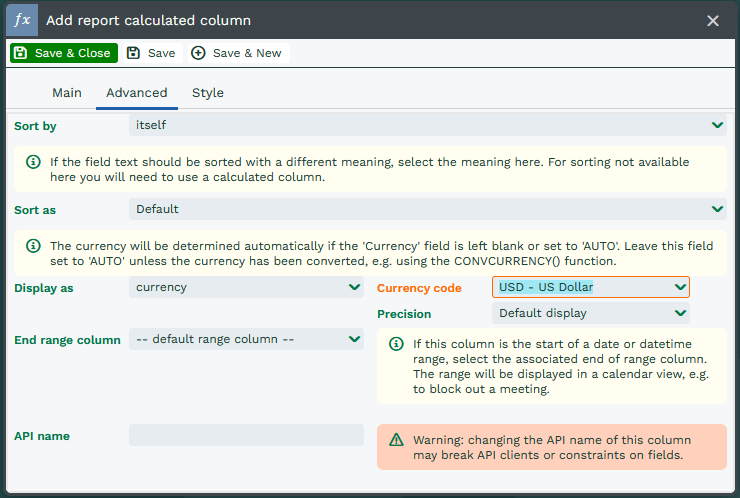
As this is a calculated column, you need to specify the Display as value on the Advanced tab of your column. Display as a currency, and select the Currency code to match to the currency used in the formula.